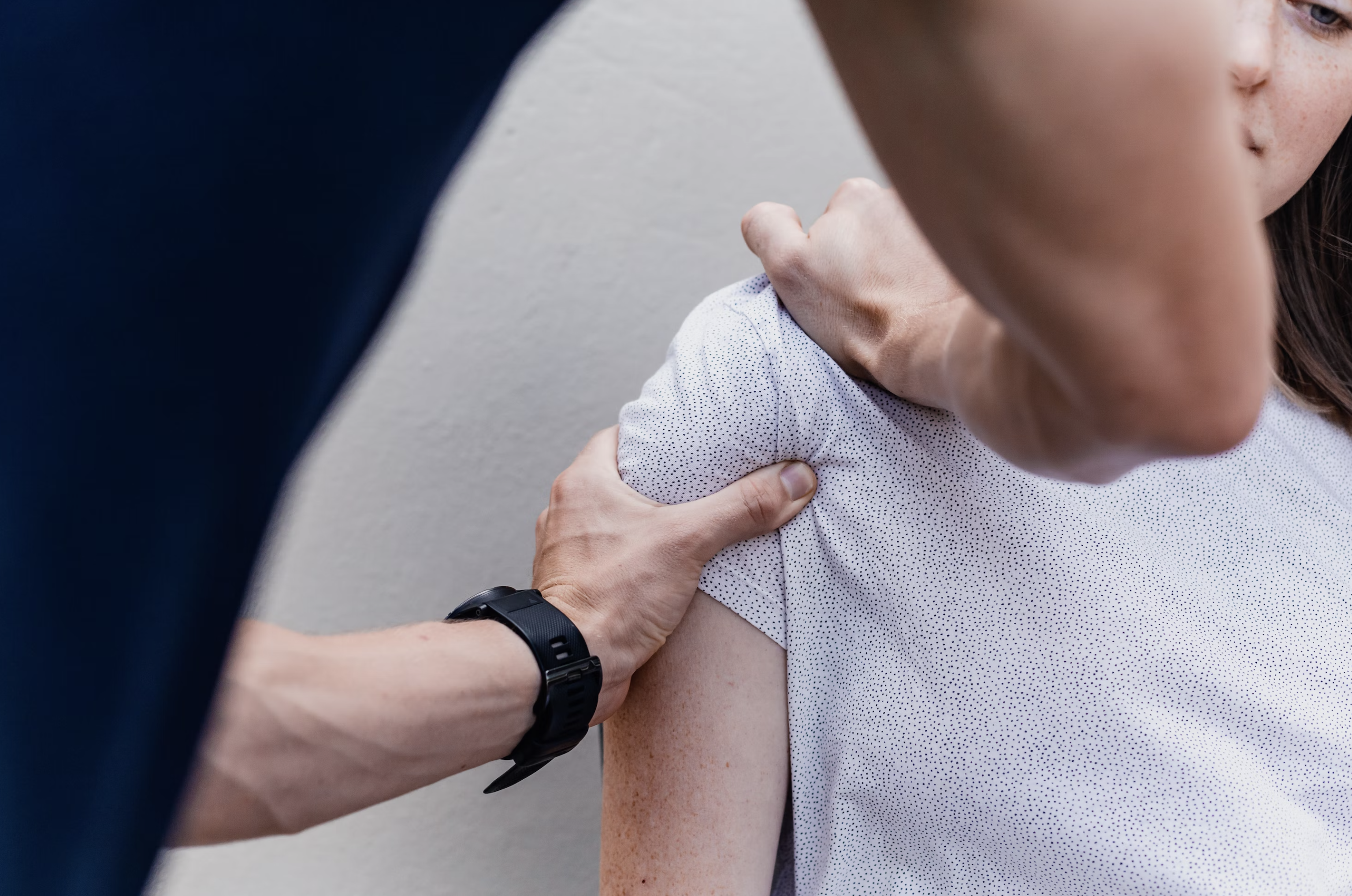
Tendinitis is typically caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the tendons. This can occur in activities that involve repetitive motions, such as throwing a ball, typing, or playing a musical instrument. Tendinitis can also occur as a result of an injury, such as a fall or a direct blow to the tendon.
Symptoms of tendinitis include pain, stiffness, and tenderness in the affected area, as well as reduced range of motion. Pain is usually worse with activities that involve the affected tendon, and may be accompanied by a creaking or crackling sound.
Treatment for tendinitis typically includes a combination of rest, ice, and physiotherapy. It’s important to rest the affected area as much as possible and avoid activities that may exacerbate the condition. Applying ice to the affected area can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
Physiotherapy treatment will typically include exercises to improve strength and flexibility of the affected area, as well as manual therapy techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and dry needling to alleviate pain and improve function. A physiotherapist will also give you guidance on how to manage symptoms and prevent further injury.
It’s also important to address any underlying causes of tendinitis such as muscle imbalances, poor posture and lack of conditioning, as well as to take steps to prevent recurrence of the condition. This may include changing your technique when performing a repetitive activity, using proper equipment and taking regular breaks.
It’s important to understand that tendinitis is a condition that takes time and effort to heal. You need to be consistent with your treatment plan and to work closely with your physiotherapist to set realistic goals for your recovery.
In conclusion, tendinitis is a common condition caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the tendons. It can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the affected area, making it difficult to engage in daily activities. Treatment for tendinitis typically includes rest, ice, and physiotherapy, with the goal of reducing pain and improving function. It’s important to address underlying causes and to take steps to prevent recurrence. If you have persistent pain or symptoms, seek professional help from a physiotherapist.
Thank you for reading,
Anthony Grande
Registered Physiotherapist
Bsc PT