Key Takeaways
-
Physiotherapy can help Arthritis is an individualized, whole-person journey. The program is designed to address mobility limitations and pain. It improves overall quality of life by focusing on specific exercises, manual therapy, and education.
-
Regular physiotherapy sessions can help alleviate arthritis symptoms by reducing joint pain, improving flexibility, and strengthening muscles around affected areas. These benefits all lead to improved joint stability and functionality in the long run.
-
Physiotherapy educates you on how to improve your posture, alignment, and body mechanics. This understanding allows you to avoid aggravating and hurting your joints while engaged in normal daily tasks.
-
Complementing exercise-based treatments, techniques such as heat and cold therapy, acupuncture, and electrotherapy offer further pain relief while promoting healing, too.
-
Collaborating with a physiotherapist ensures a tailored plan, offering strategies for self-management, assistive devices, and practical tips to maintain an active and independent lifestyle.
-
Be diligent about your physiotherapy exercises. Implement ergonomic practices in the home, and remain in consistent contact with your physiotherapist to maintain healthy joints long-term and manage arthritis effectively.
Living with arthritis can make even the simplest tasks difficult, but physiotherapy can help you find the best approach to relieve pain and restore movement.
By placing emphasis on personalized exercises, joint-friendly techniques, and effective pain management strategies, we work to alleviate stiffness and build muscle strength. This helps optimize joint function and encourages healthier movement patterns, which in turn helps joint health while improving quality of life.
Through regular treatment, physiotherapy will help arthritis sufferers reclaim their independence and return to an active lifestyle. Here’s how it can help make a difference in a tangible way.
Importance of Physiotherapy for Arthritis
Physiotherapy is integral to treatment and management of arthritis. It is vital to restoring movement and increasing the overall quality of life for people with joint damage. This treatment is particularly effective for those suffering from arthritis of the hands, knees, hips, or spine.
Approximately 70% of individuals with arthritis experience pain in these locations. Through an individualized plan of care with a physiotherapist, patients can develop the tools to effectively handle pain, increase their range of motion, and ultimately stay independent.
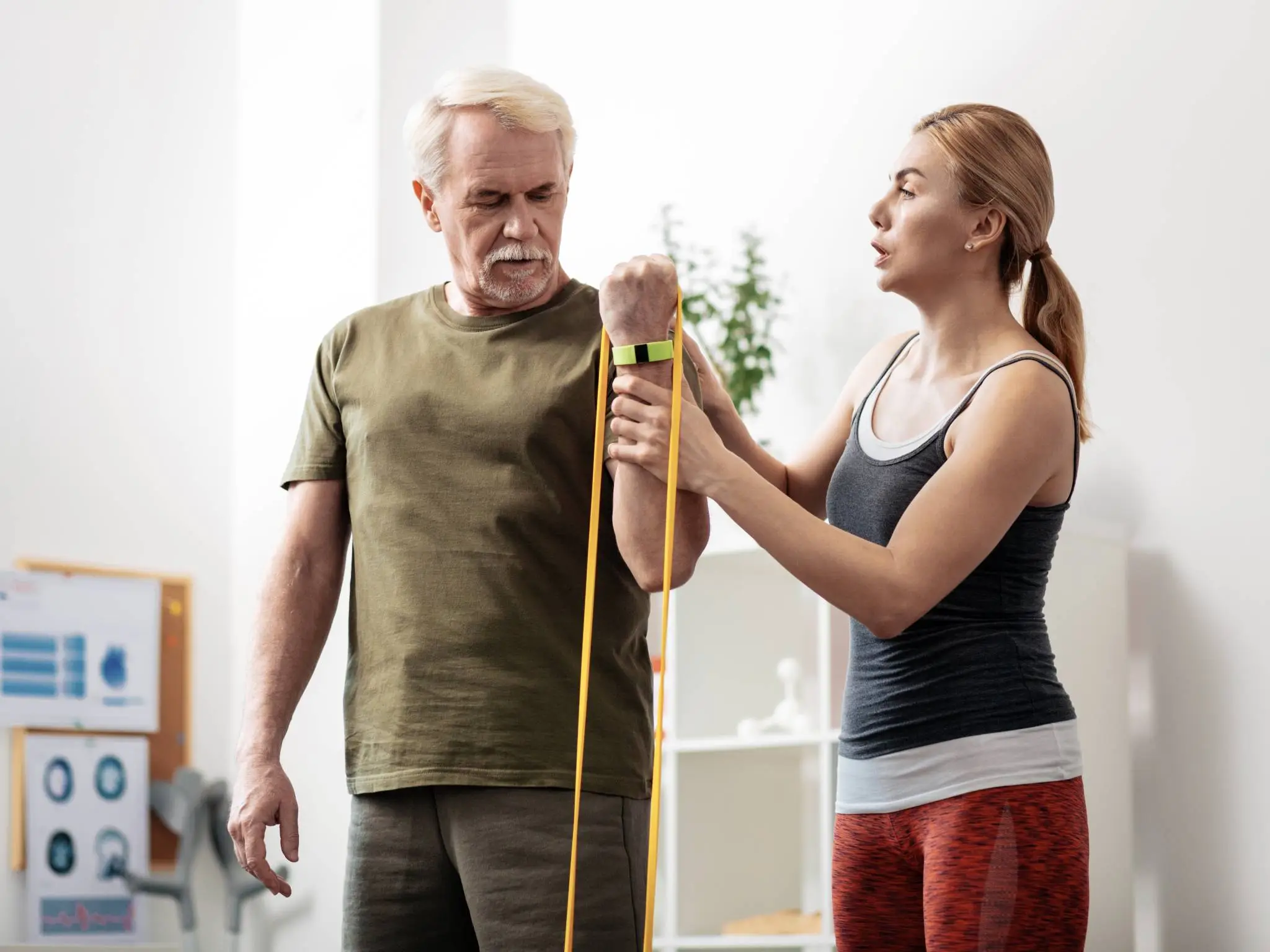
Staying active is one of the most important components of physiotherapy for arthritis. Though this may feel counterintuitive, light movement is critical for avoiding additional joint stiffness and damage. A physiotherapist, for instance, may suggest low-impact stretching or resistance training exercises to maintain flexibility and muscle strength in the joints.
These activities not only assist with pain control but brace the neighboring joints, lowering subsequent stress. With their specialized training, physiotherapists are able to offer strategies to improve daily function. For instance, they will teach a patient to modify their alignment when sitting or walking.
They’ll train them on safe lifting and bending practices to reduce strain on their joints. You can even utilize therapeutic methods such as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) therapy when treating pain. Research has found that just one session a week for four weeks can produce significant results.
You can relax sore muscles and improve blood flow by applying hot packs. Use them for 10–20 min, 1–2 times per day. Physiotherapists should recommend less frequent check-ins rather than weekly visits. This method empowers patients to monitor their own progress and update their programs as needed.
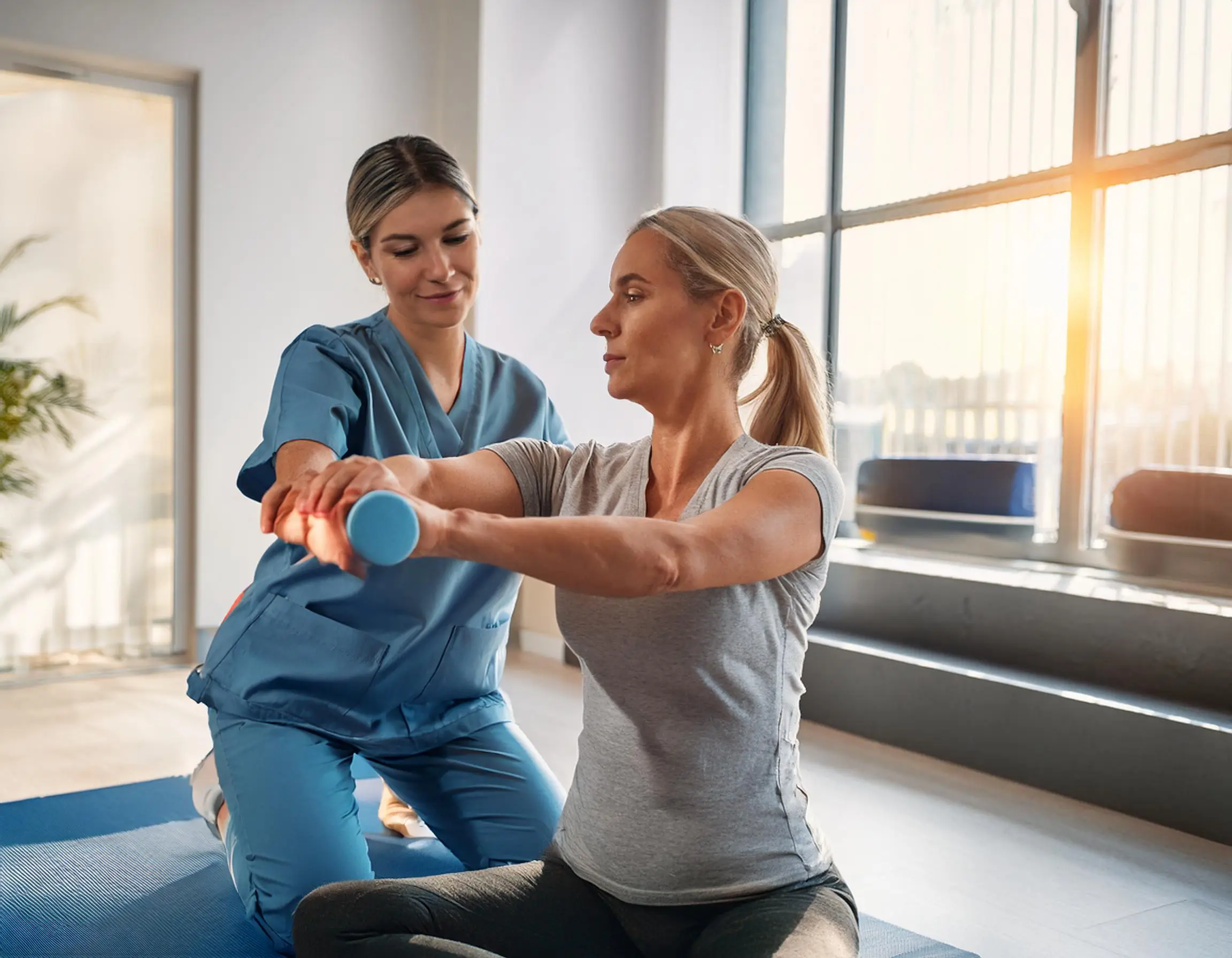

How Physiotherapy Helps Arthritis
Arthritis is a chronic lifelong condition. It addresses the physical and emotional burden patients experience. Using personalized, targeted strategies, it’s proven to deliver measurable improvements in pain relief, mobility, range of motion, strength, and overall quality of life.
Here are just a few of the important ways physiotherapy improves the quality of care for patients with arthritis.
Reducing Pain and Discomfort
Pain management is usually the first consideration for people with arthritis. To help reduce stiffness in arthritic joints, physiotherapists use techniques such as manual therapy, which involve hands-on manipulation. They use modalities including heat, cold therapy, ultrasound and electrical stimulation to ease pain.
These approaches not only address acute pain but foster chronic pain relief as well. Along with these treatments, physiotherapists place a strong focus on self-management strategies. For example, we can educate patients on modifying their activities of daily living.
We guide them in using adaptive devices such as compression gloves to relieve pressure. When used together, these strategies empower patients to take charge of their pain, and 80% of patients experience considerable improvement following physiotherapy.
Enhancing Joint Flexibility and Range
One of the most common issues caused by arthritis is stiffness, making it difficult to move. Physiotherapy emphasizes stretching exercises specifically targeted to the affected joints that slowly help restore flexibility and make movement smoother.
For instance, mild stretches for hip or knee arthritis may improve flexibility and make walking easier. Every step of the way, progress is carefully monitored, with modifications to increase or decrease difficulty, keeping exercises challenging, but always doable.
Patients are motivated to practice diligently; the practice improves their joint health and avoids further progression of stiffness.
Strengthening Muscles Around Joints
Weak muscles may put extra strain on arthritic joints, increasing pain levels. Physiotherapists develop targeted strengthening exercises that address weak muscle groups in the body. For instance, they develop specific quadriceps exercises to treat knee arthritis, shoulder stabilizers in patients with upper-body arthropathies.
This supplemental support takes pressure off the joints and increases the range of function. Ongoing evaluations monitor muscle strength gains, making sure that each patient’s program is maximized.
Physiotherapists help patients understand how stronger muscles help protect joints, motivating patients to stick to their routine.
Improving Posture and Alignment
Poor posture can exacerbate joint pain. Physiotherapists evaluate alignment and identify habits contributing to discomfort. Corrective exercises, like core strengthening or back stretches, address these issues, while education on proper body mechanics helps prevent strain during everyday tasks such as sitting or lifting.
Boosting Stability and Balance
Joint instability from arthritis puts you at greater risk of falling. Activities like standing on one leg or working with stability balls improve coordination and promote confidence. We take an objective look at each individual’s balance abilities to develop balance-specific interventions to address each person’s unique needs.
Daily practice increases balance and reduces risk of falls.
Goals of Physiotherapy for Arthritis
While arthritis may be affecting your daily life, physiotherapy can make real improvements by addressing your specific needs. By identifying objectives that set realistic expectations, we can work with patients to better manage their symptoms, improve their mobility and boost their quality of life. Here’s how we approach these objectives:
1. Relieve Symptoms and Pain
Managing pain is a primary goal for people with arthritis. To test treatment efficacy, we established clear, measurable goals for pain management, monitoring improvement objectively over time. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) techniques marvel in pain relief. Research indicates that when prescribed weekly they can cut pain for at least 80% of patients.
We bring in hands-on techniques, including manual therapy, heat or cold applications, and acupuncture, to treat one-of-a-kind pain-related symptoms. Open communication is essential in this process. When we encourage patients to communicate their level of pain and daily experiences, we’re better able to tailor treatment plans in real-time.
If a patient is complaining of pain with an exercise, we are immediately modifying that exercise. We start to move away from more aggressive motions but still keep them moving forward.
2. Improve Mobility and Functionality
Arthritis often limits movement, but targeted exercises can help restore mobility and functionality. We begin by assessing each patient’s functional limitations, such as difficulty climbing stairs or bending joints, and create personalized plans to address these challenges. Gait and balance training are particularly useful for individuals with osteoarthritis in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
By improving gait patterns and stability, we reduce the strain on affected joints. Change takes time and purposefulness. For example, a patient with a lot of stiffness may need to focus on range-of-motion exercises first, then move on to strengthening exercises.
Continual reassessment can help make sure that what they’re doing is still challenging and appropriate for the patient’s changing skill level.
3. Enhance Quality of Daily Life
Arthritis can make performing easy tasks, like buttoning a shirt or cooking a meal, difficult. We first determine what areas of daily life are most affected by arthritis symptoms and then work on developing strategies to help them participate. For instance, educating about joint protection methods can allow patients to reduce stress on joints while performing everyday tasks.
Engaging the patient in establishing these goals helps to encourage and motivate the patient to remain engaged. A gardening enthusiast patient, for example, might do hand exercises specifically to prevent loss of grip strength. This will allow them to return to their beloved horticultural avocation!
So this focus on what you’re personally interested in helps make sure that therapy feels worth it and purposeful.
4. Prevent Further Joint Damage
Joint protection is another long-term goal of physiotherapy. We teach patients how to protect their joints, like by using assistive devices or changing how they do something to ease the strain on joints. We incorporate prevention into treatment plans. These goals can involve activities like strengthening surrounding muscles and working to improve posture to reduce the risk of injury.
Regular assessments allow us to monitor joint health closely. By evaluating factors like range of motion, muscle strength, and gait patterns, we can identify potential issues early and adjust interventions accordingly. Educating patients about osteoarthritis management and lifestyle modifications empowers them to make informed decisions about their health.

Techniques Used in Physiotherapy for Arthritis
Managing arthritis can require a multi-faceted approach, and physiotherapy provides a variety of techniques that can be personalized to fit the individual needs. These approaches focus on pain relief, improving mobility and quality of life.
Here are some of the main techniques physiotherapists employ to help treat arthritis and its symptoms.
Exercise Programs for Strength and Flexibility
Creating individualized exercise regimens is a mainstay of arthritis treatment. These exercises focus on strength and flexibility. They provide support to injured joints and muscles, while helping to maintain their range of motion.
Gentle stretching exercises can help reduce tightness in your joints. Additionally, as resistance training builds up the muscles around your joints, this adds additional support to your joints.
Including a wide range of exercises is key to working multiple muscle groups and joints. Aerobic exercise such as swimming or cycling improves lower body mobility.
Simultaneously, hand exercises increase dexterity for patients suffering from arthritis in their hands. By participating in consistent exercise programs, long-term effects are maintained, allowing patients to carry out daily activities with more efficiency and ease.
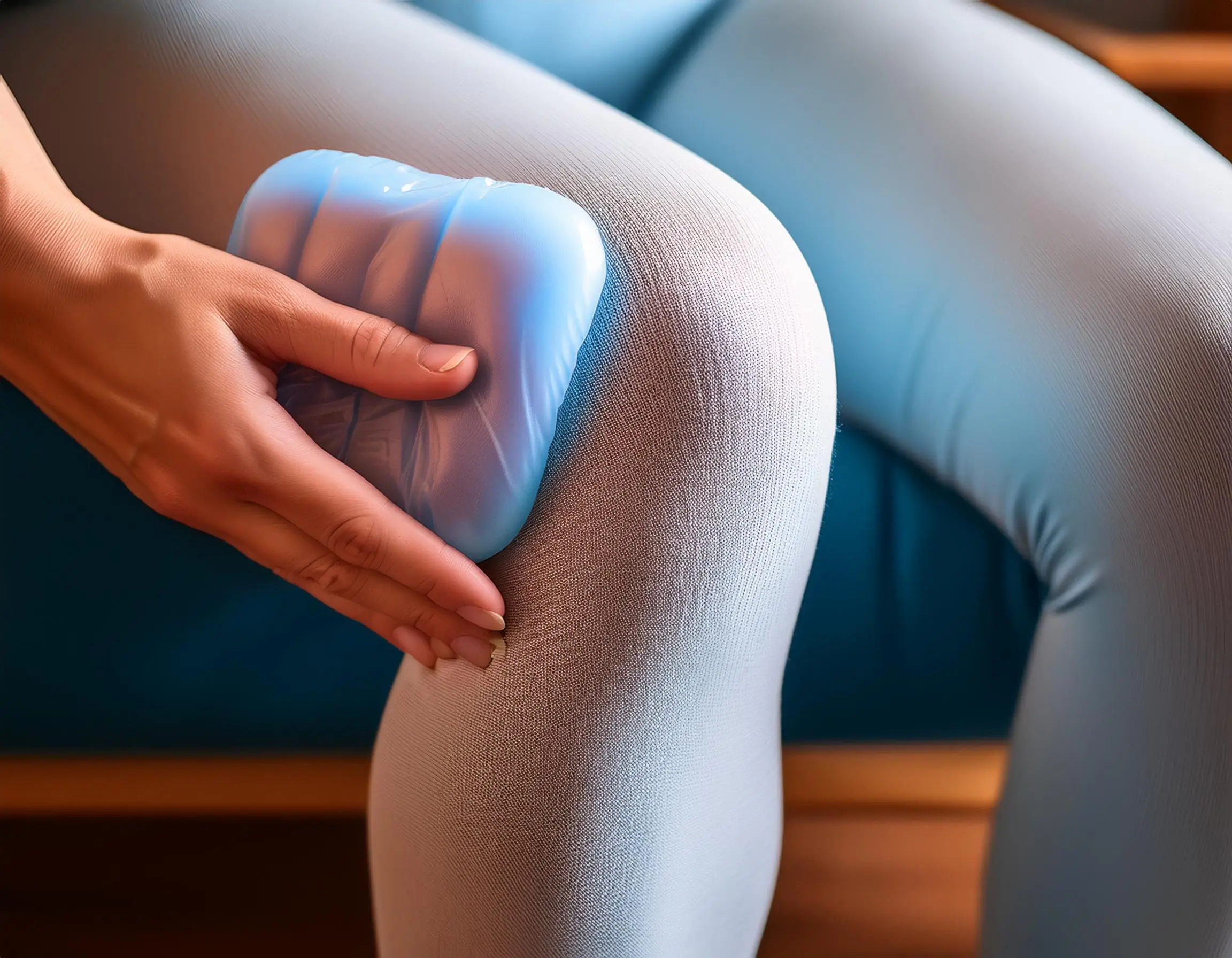
Application of Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapies provide easily accessible and cost-effective methods to alleviate arthritis symptoms. Heat therapy relaxes tense muscles, improves circulation, and provides soothing relief for stiff joints.
Warm compresses or heated pads can be used on affected areas, particularly before exercise. Cold therapy decreases inflammation and numbs painful areas in the process.
Ice packs work best after heavy activity or during a flare-up. Patients are educated in the use of heat to relax the muscles and cold for inflammation.
This gives them the skills and knowledge to better manage their symptoms on their own between sessions.
Use of Acupuncture for Pain Relief
Acupuncture can be a valuable adjunct to your arthritis management plan. Very thin needles are inserted into specific points on the body to stimulate nerves, release endorphins, and increase blood flow.
This technique holds great potential for reducing pain, especially for those suffering from long-term arthritis conditions. When acupuncture is included as part of a multifaceted treatment approach, patients with arthritis can reap the pain-relieving benefits of acupuncture in combination with other physiotherapy techniques.
It’s effective, low-impact, and safe – and it can easily be adapted to individual severity of disease and level of comfort.
Electrotherapy Methods for Arthritis Treatment
Electrotherapy is a technique that uses electrical currents to relieve pain and accelerate tissue healing. Other techniques like Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) pain triggers and stimulate the body’s natural painkillers.
Ultrasound therapy, another technique, improves blood flow and decreases swelling in the joints that are affected. Physiotherapists guide patients in understanding how electrotherapy works and its suitability for their specific arthritis type, ensuring a personalized approach that addresses individual symptoms.
Role of Physiotherapists in Arthritis Care
Physiotherapists play a diverse and essential role in managing arthritis. By combining clinical expertise with a patient-centered approach, they aim to improve joint health, reduce pain, and enhance overall mobility. Their work often begins with a comprehensive assessment, evaluating factors like gait, daily activities, joint range of motion, muscle strength, posture, and even respiratory function.
These insights help create a well-rounded picture of each patient’s unique situation, allowing for targeted interventions that make a meaningful difference in day-to-day life. Physiotherapists are not just exercise gurus though; they focus on empowering patients through education. This involves providing education about osteoarthritis (OA), appropriate management strategies, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
Patients receive education on how to protect their joints during everyday activities and avoid putting unnecessary stress on them which could make their condition worse. Physiotherapists play important roles in improving gait patterns and balance. In turn, this reduces the risk of stress on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips, encouraging improved long-term outcomes.
Creating Personalized Exercise Plans
Physical activity is important for arthritis management. Physiotherapists are experts at creating individualized exercise plans that work with each person’s specific needs and goals. These plans begin with detailed evaluations, considering the individual patient’s flexibility, strength, and particular physical restrictions.
For example, an individual with hip arthritis might be advised to seek relief with low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming. Another patient might need strength-based exercises to improve their knee stability. Patient preferences are taken into account as well, making exercises effective and fun at the same time.
For instance, if a patient really likes to be around people, encourage them to take yoga or t’ai chi classes to meet others. These classes are a great way to improve flexibility and relieve stress. We continually monitor and reassess the exercise programs to address your improvement and continue to push you to new goals. This ensures that the plans remain flexible and sustainable.
Providing Guidance on Pain Management
Pain management is another key area in which physiotherapists play an invaluable role. More practical strategies such as hot or cold therapy can be easily incorporated into daily routines.
Applying a hot pack for 10 to 20 minutes once or twice a day can help relieve morning stiffness. Conversely, the use of cold packs post-activity is a great way to minimize swelling. Patients are likewise trained to recognize triggers of pain and employ pain management strategies like pacing themselves with physical activity.
This is where communication comes into the picture. Continuous communication regarding pain intensity allows the physiotherapist to adjust their approach and reassure the patient that they are not alone in dealing with their symptoms.
Recommending Assistive Devices for Support
For many patients, these assistive devices are life changing, offering a new level of mobility and independence. Physiotherapists have the expertise to determine the specific individual needs to recommend the best, most appropriate option, be it a cane, walker or custom orthotic.
They offer step-by-step instruction to help you use these devices safely and effectively. This allows patients to derive the full benefit while minimizing stress on compromised joints.
Educating Patients on Proper Movements
Avoiding stress to joints and practicing proper body mechanics are important when it comes to preventing injury. Physiotherapists teach patients how to move safely during everyday activities, like lifting objects or bending down, to minimize stress on vulnerable areas.
Therapy sessions bring all of these lessons together for real-world practice. By doing this, patients are able to gain confidence in using the movements in everyday scenarios. Proper practice mechanics will have ripple effects in the long run, preventing additional damage to your joints.
Benefits of Physiotherapy for Arthritis Patients
Restoring Joint Functionality
Physiotherapy has an important role in combating arthritis by restoring joint functionality with rehabilitation exercises tailored to individual needs. These included range of motion exercises to keep joints flexible. They assist you in regaining the range of motion you need to perform essential tasks such as walking, bending, or even opening a jar.
Specific strengthening exercises help strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joints, offering extra support and stability. This can result in clear improvements over time in how smooth and comfortable a joint moves.
Monitoring progress is another essential step in this process. Frequent evaluations with a physiotherapist give patients and providers an opportunity to track progress with joint movement and overall functionality. This improves the likelihood that treatment plans stay effective, personalized to the patient’s needs.
Active participation in the rehabilitation process further maximizes these advantages. Patients who consistently perform their exercises as prescribed and take an active role in their care will notice quicker results. They experience longer-lasting results.
This partnership between patient and physiotherapist helps establish a solid framework for obtaining optimal results.
Reducing Dependency on Medications
For arthritis patients, physiotherapy provides a path to lessening their dependence on pain medications. By utilizing non-pharmacological methods such as manual therapy, guided exercises, and modalities, physiotherapy allows patients to manage their pain in a more natural way.
Heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and acupuncture can relieve pain. These techniques are effective at providing relief without the need for additional medication.
Less reliance on medications could help improve patients’ overall quality of life in a major way. With fewer side effects and a lower risk of dependency, patients are frequently more in control of their health.
Encouraging patients to try these options out with their physiotherapist deepens their pain management plan on multiple levels. This strategy leads to safer and more effective outcomes.
Promoting Long-Term Joint Health
Keeping joints healthy is important for preventing additional damage and promoting long-term mobility. Physiotherapy equips patients with the tools they need to help safeguard their joints. It educates them about body mechanics and incorporates low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling into their daily life.
Preventative measures are an integral part of treatment plans. Effective weight management strategies can go a long way. Even modest weight loss will make a meaningful difference in the stress put on joints, particularly for people with arthritis in weight-bearing joints such as the knees.
Consistent follow-ups with a physiotherapist help to perfect these strategies, making it easy to adjust them as patients’ needs change.


